PJ Hagerty, Head of Developer Advocacy at Mattermost and Board Member of Open Sourcing Mental Health (OSMHhelp.org). The organizer of DevOpsDays Buffalo, CodeDaze and ElixirDaze, a developer, writer, speaker and musician, spoke about the philosophy of the modern world of software development.
People constantly have new needs, for the satisfaction of which they invent more and more new technologies. A great example of constant progress is the transformation of how information has been transmitted since the 19th century. In 1860, the Pony Express delivery service appeared in North America, which lasted only a month and a half and became irrelevant – it was replaced by the telegraph.
The same processes can be observed in software development – others are replacing some methodologies.
Table of Contents
Waterfall
The Waterfall model is a linear, sequential way in designing software development, where progress flows in one direction – downwards like a waterfall, through the stages of concept, initiation, analysis, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
There is nothing complicated in the model:
- you set the requirements;
- design software based on them;
- implement the project;
- test it;
- implement and maintain in the process of use by the end user.
But what prevents its use? The fact that the development process here is not flexible. That is why this approach was doomed to failure.
Agile methodology
Let’s look at the Agile methodology – a more modern take on. It’s a software development approach in which requirements and solutions emerge through the collaborative efforts of self-organizing, cross-functional teams. It is characterized by adaptive planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, continuous improvement, and rapid and flexible response to change.
If your team can work without a fixed schedule, Agile is the way to go.
DevOps
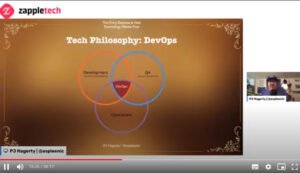
Agile has led us to something new – DevOps. It is a set of software development practices that combine direct development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops) to shorten the system development life cycle by patching and updating features in line with business goals. The primary purpose of DevOps is to process automation to reduce risks.
But this approach also has its drawback – it is based on the ideal world where everything functions. It is different in reality.
Alternative development methodologies
TDD – you must test everything you create (software, hardware, databases) before launch. But it has a disadvantage – time-consuming.
TDD is based on how users interact with the product in creation.
SDD is based on the principle of creating a product that we will not be ashamed of in front of the person using it.
Conclusion
Innovation is the key to what we do. Being a developer or QA means constant learning. Forget about the concept of MVP – work on creating a minimum VALUE product!