Automated QA Audit And Assessment


QA Audit and Assessment With Us
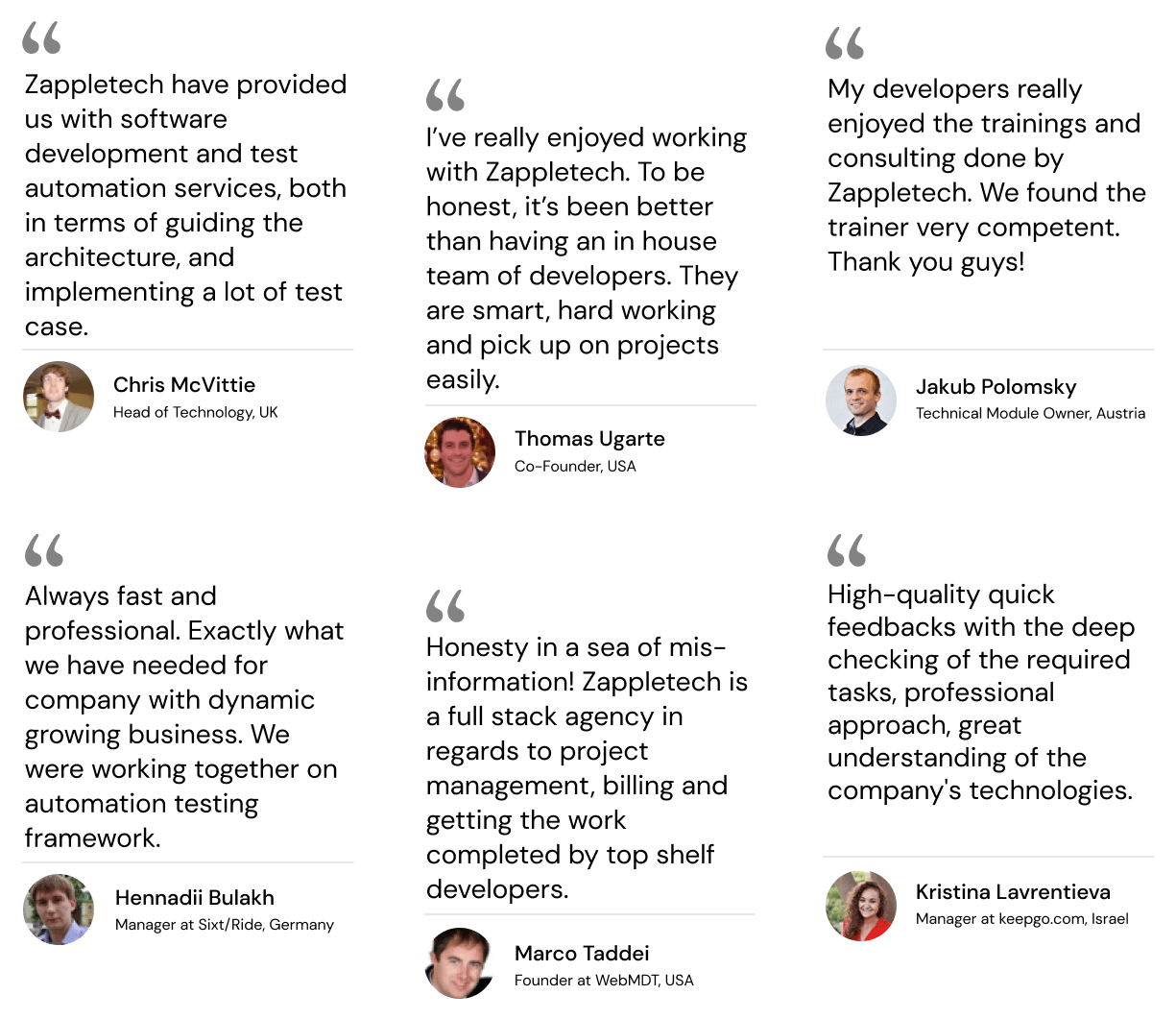
What Our Customers Say
What Is the Difference Between Quality Control and Quality Assurance?
- A quality control audit entails examining the final product for aspects that could be improved, corrected, or otherwise addressed.
- A quality control audit looks for problems that are already existing and determines how to fix them.
- The goal of quality control audits is to avoid defects in the first place.
- The goal of a quality assurance audit is to improve, if necessary, the procedures that lead to the final product.
- Quality assurance audits are a proactive, rather than a reactive, strategy.
- QA identify potential risks early in the development process.
How Does Quality Control Audits Work?
Industries We Work With
Our Expertise

Our QA Audit and Asessment at a Glance

Start Cooperation Now!
Why Should You Choose Quality Assurance Audit Services?
Maintaining robust quality control is crucial for businesses aiming to stay competitive. As customers become wiser and more competitive, excellent service quality and product allocation are critical factors in the current state. This is where QA and monitoring services act as a linchpin, linking the two.
Quality Assurance Audits (QA) are the backbone of a robust quality assurance framework. They provide a structured and comprehensive process for examining processes, products, and services, identifying solutions, and ensuring adherence to established rules. These audits are not just about compliance; they are a powerful tool for strengthening standards, fostering innovation, and consistently delivering optimal performance in the industry.
Considering the complex nature of quality audits and assessment services provided in this era, this article explores both in detail, showing their great impact on the modern market. We will discuss the pivotal nature of QA audits in ensuring efficient and productive systems by upgrading their management systems.
Readers’ presentation of this topic is expected to happen in depth. It will include the concern of quality assurance and assessment services, the definitions and purposes of these services, the fundamental components that aid in conducting a quality audit, and the numerous gains that result from investing in these services. First, we will explore hands-on case studies where companies have involved in quality assurance audits to grow the quality and efficiency of the entire process and performance overall.
As part of the solution, we will also discuss the associated system difficulties of QA audits and provide feasible solutions. We will brief on the latest trends and developments within the QA audit horizon to enable businesses to foresee future trends in quality assurance practices and the directions to adapt to stay ahead of the curve at all times.
Whether you’ve already been working as a seasoned quality assurance officer in case studies, helping your organization to take business quality assurance to the next level, or maybe you are the chief manager looking for the excellence-elevating strategies, this is exactly the article you were looking for as far as it provides useful advice and actionable steps to cover the needs of a modern quality assurance and assessment services provider. Look out for this trip as we discuss QA audits about their impact in organizational prosperity.
Understanding Quality Assurance Audits
Quality Assurance Audits are a cornerstone of a strong quality management system and are made up of standardized processes through which the organizations are evaluated to ensure the quality and conformity of products, services, and processes. In that respect, the auditors’ mission is to ensure that all result products meet the standards consistently, thus improving customer service, decreasing organizational risks, and maintaining excellence
Conducting a quality assurance audit is a systematic process wherein an organization evaluates and examines its quality management system, processes as well as practices in the place of work. One of the main objectives of the regulation is auditing and identifying gaps where the system is non-compliant, and proposes suggestions on how business performance can be improved by the organizations establishing the standards of quality, hence upholding them. Frequent quality assurance assessment will help organizations detect problems before they are out of control and avoid errors that will increase workload, improve processes, and achieve maximum productivity and effectiveness.
Quality assurance audits are designed differently from each other, and depending on operations, a specific type is used. Such procedures can be of a process review type, product review type, supplier audit type, and system audit type, among others. Each audit variant would be indispensable because it would be dedicated to one of the following tasks: evaluating the effectiveness of the internal processes or assessing the quality of the produced commodities, or guaranteeing the conformity with the industry standards and norms.
Frequent quality control evaluations, undoubtedly, are of the highest priority, mainly because of the context of the modern complex business milieu. Through manufacturing processes, businesses deal with the increasing problem of creating new items and keeping up with clients and their evolutions. Quality audits contribute to organizations developing a productive model of quality management practice, almost prevention of not an active step to maintain systems of highest quality standards.
In summary, quality assurance audits play a vital role in helping organizations uphold high quality standards, mitigate risks, and drive continuous improvement. By conducting regular audits and leveraging the insights gained, businesses can proactively address issues, optimize processes, and unlock new levels of excellence across their operations.
Key Components of Quality Assurance Audit Services
Preparing for a QA Audit: Planning and Documentation
Before renewing a quality assurance (QA) audit, it is important to plan well to ensure that the audit process will run quickly, efficiently, and perfectly. The planning stage is key to this process. It entails the beginning of the work involving careful and thorough preparation of all objectives, criteria, and procedures required during the audit.
Setting Objectives | The initial step before a QA audit is to set out the objectives and scope of the audit. This will cover choosing targets and the audit processes that need to be examined and giving the specific goals for the audit and its objectives. |
Developing Audit Criteria | After this, evaluation criteria should be created to rate the organization’s quality standards, regulatory needs, and organizational policies. Such criteria help define the areas or issues against which the audit results will be assessed. |
Creating Audit Plans | An audit plan is a subdivided roadmap that shows audit routes, timeframes, available resources, and duties. It covers the integral part of conducting all audits, with the aim of having the same values everywhere in the process. |
Gathering Documentation | The filing of comprehensive documentation is vital to any auditing process. This consists of getting records and documents, such as policies, procedures, and so on, that are needed to assess performance and compliance. |
- Execution Phase: Conducting the Audit Process Effectively
Once the preparations are complete, the audit enters the execution phase, where auditors conduct on-site assessments, interviews, and examinations to gather data and evidence.
Conducting Interviews and Observations | Auditors get close to the staff who work at different levels that include the systems, procedures and issues the organization deals with. They could personally go through process steps to validate compliance and pinpoint places to improve if they witness operations in action. |
Performing Document Reviews | The auditors review every piece of evidence, triple-checking to see if all processes, rules, and regulations have been followed. They also review logs, reports, audit history, records, and any other related documentation to verify its accuracy and completeness. |
Utilizing Audit Tools | Numerous means and methods are applied throughout the audit to help with data gathering, analysis, and reporting. These methods are embodied by instruments such as checklists, questionnaires, statistical sampling techniques, and audit management software. |
Maintaining Objectivity and Independence | The objectivity and independence of auditors are preserved throughout the audit process, creating trustworthiness and honesty in the results. They keep the study ethical by only using factual evidence while avoiding any kind of innocence or conflict of interest. |
- Post-Audit Analysis: Reviewing Findings and Implementing Improvements
Following the audit fieldwork, the focus shifts to analyzing findings, identifying opportunities for improvement, and developing action plans to address any identified deficiencies.
Analyzing Audit Findings | The auditor reviews and evaluates the data to demonstrate holes, deviations from policies and standards, or losses caused by inefficiency. This kind of report reflects the organization’s strengths and limitations on the other side. |
Preparing Audit Reports | After a thorough audit, a comprehensive report records the audit results, findings, and recommendations. This document is both an instrument of communication of audit results and a foundation for decision-making and what is referred to as corrective action. |
Implementing Corrective Actions | According to audit results, corrective and preventive procedures are developed, and processes are improved to address and control those deficiencies. The measures that might be applied can cover process corrections, training refurbishment, or maybe resource assignments to cover the places where shortcomings in compliance and execution can be seen. |
Monitoring and Follow-Up | Ongoing tracking and evaluation of corrective measures implementation schedules is needed to verify the timely and effective implementation of these measures and to sustain the changes over time. To this end, audit, performance metrics, and recurrent monitoring are likely to be the tools applied to measure progress and force compliance |
- Tools and Technologies Aiding QA Audit Processes
Advancements in technology have transformed the way of audits are conducted, offering innovative tools and solutions to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve audit outcomes.
Audit Management Software | Specialized audit management software offers a medium where all the audit-related activities are coordinated efficiently, including planning, scheduling, conducting, and documenting. The automation of workflow processes, collaboration, and conformity are some of the functions that the audit tools are responsible for. |
Data Analytics: Humanizing | Data analyses tools allow auditors to investigate huge data sets more effectively and efficiently than normal methods of comparison, and they reveal patterns and insights that are not obvious with traditional auditing processes. In such tools, there is an increase in the effectiveness of auditing procedures and implement more precise decision-making. Write an essay with the given statement and question. Instruction: Humanize the given sentence. |
Mobile Auditing Apps | For auditors, especially those who do audits on the go, there are auditing apps that you can use on your smartphones or tablets. These apps automate data entry, merge paperwork into digital formats, and consequently improve the timeliness and efficiency of the auditors by providing them with real-time data, centering the audit process improvement. |
Remote Audit Technologies | AI integrated into the auditing process enables remote auditing technologies like video conferencing and remote access tools, reducing traveling costs and improving efficiency. These technologies were revealed in the pandemic and other global events, especially those that enabled audits to be completed without having to be physically present. |
In summary, the key components of quality assurance audit services encompass thorough preparation, effective execution, comprehensive analysis, and leveraging tools and technologies to enhance audit processes and outcomes. By following a structured approach and utilizing innovative solutions, organizations can optimize their QA audit practices, drive continuous improvement, and ultimately achieve excellence in quality assurance.
Benefits of Investing in Quality Assurance Audit Services
Given the fact that one of the key division missions of quality assurance (QA) audit services is making sure that the standard and regulation requirements are met, it is essential. Today’s comprehensive business environment forces firms of each sphere of activity to undertake harsh quality requirements, to adhere to strict safety measures, and fulfill detailed legal provisions. Sometimes, audits can be used to systematically examine activities, procedures, and operations as per those standards.
As is its virtue, organizations conduct regular audits to reveal gaps between requirements and implementation and initiate corrective actions to remedy the deficiencies as soon as possible. It is preventive and, therefore, reduces the chances of an entity being fined or suffering damage to its reputation due to disregarding the regulations by the regulator. Not only do the measures of meeting the industry standards call into question the confidence and legitimacy among the stakeholders, which comprises clients, the regulator, and the business partners.
Determining what risks are likely and taking steps to lessen them before the main risk.
The risk identification and proactive mitigation valued as another positive QA audit service characteristic is another manifest of this sector. Risk Management is one of the fundamental aspects of quality control as organizations are supposed to forecast and get through risks in their operations, reputation, and bottom line.
The comprehensive risk assessment capability during audits enables organizations to detect any possible threats, weak areas, & single spots where there might be a failure. Thanks to this thunder since impact risk identification, they can use preventive measures and controls to mitigate risks at the beginning when they are not big problems anymore. Whether it is detecting the supply links’ unsteadiness and unwanted safety conditions, cyber security implications or other individuals of QA, audits empower organizations to protect their interests and stay ahead of various risks.
Enhancing Product/Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Utilizing a audit service for the product/service is thus a direct way to improve the quality and bring memorability and satisfaction among customers. Today, when there is increased competition in the marketplace and when clients have high expectations of not only goods and services but more a need for excellence, quality plays a significant role. A QA audit will hold up a mirror to the organization’s quality matrices to spot areas of poor performance to help uplift the same process, performance, and innovation in the eventuality.
Through the meticulous XYZ of product/service quality in audits, organizations can determine what is not good, what is not as good as it should be, and what areas should be improved. So this, in some way, allows them to rectify those steps that go wrong, refine the processes, and do quality control correctly to create the ultimate products/services for their customers. Therefore, organizations may increase the positive feedback from customers and their loyalty to the brand, which is the key source for the long-term flourishing of the business.
Boosting Organizational Efficiency and Profitability
Furthermore, involving QA audit services can positively influence the productivity and profitability levels of the business. Ineffective operations, problems with quality management, and operational frame-ups negatively impact productivity, resource utilization, and profitability.
The feedback and corrective measures prescribed in the audits of QA by the organizations lead to improved workflow efficiency, shorter cycle production times, and reduced production expenses. This contributes to optimal resource consumption, a better productivity level of the firm, and greater profitability. On the other hand, by cultivating the habit of persistent improvement and leading in quality, quality audit provides environments to respond to changeable markets’ dynamics, involve opportunities, and keep up the continuity.
In concluding this thought, an organization that invests in quality assurance audit services gives out numerous benefits, including meeting quality standard requirements, averting proactive risks, and definitively improving the quality of production as well as the organizational efficiency and profitability. This can be achieved utilizing ensuring quality control and evaluation procedures. This is a key factor in the development of organizations that can become successful in all terms of changing business environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quality assurance audits stand as a cornerstone in pursuing organizational excellence, offering invaluable insights and opportunities for improvement across various facets of operations. Throughout this exploration of quality assurance and assessment services, we’ve delved into the multifaceted benefits of investing in the audit of QA practices, recognizing their transformative power in driving sustainable growth and success.
Recap of the Importance of Quality Assurance Audits in Unlocking Organizational Excellence
Quality compliance audits, as a crucial pillar, focus on conformity with industry specifications, risk management, and product improvement, bringing operational efficiency and profit growth to the organization. Through the intent and execution of regular auditing, identifying the spots for development, and taking the corrective arias, firms can excel and become a source of the edge. Using the audit, organizations strive for excellence and success in today’s highly competitive business world.
Final Thoughts on the Transformative Power of Investing in QA Audit Services
The realization that our discussion has yielded some invaluable insights has made it evident that there cannot be a case for cutting corners and dismissing quality assurance audit services as just a compliance exercise but as a critical strategic imperative to the wellness of organizations in a highly competitive landscape. The dramatic effect occurs because QA audits scan hidden inefficiencies, mitigate risk, and drive continuous improvement for all aspects of the processes. Through the adoption of an active quality management system, companies will boost customer satisfaction ratings, enhance trust with the stakeholders as well as secure the enviable spots for the long
Prioritize Quality Assurance in Their Business Strategies
Because of the numerous advantages that this quality assurance audit holds, quality assurance should be the core value of the organization’s strategy. Whether a small or a large enterprise, investing in audit services will give the investors a chance to reap great profits in improved quality, decreased cycle times and growth continuously. Therefore, I not only necessitate readers to implement a quality assurance approach prioritizing improvement and status quo maintenance, but I also advocate for establishing a culture of excellence and continuous improvement in the organization.
In conclusion, quality assurance audits are not mere compliance exercises but strategic instruments that open up an extraordinary opportunity for organizations to achieve excellence and remain competitive in a rapidly paced and dynamic marketplace. Employing QA audit services, organizations can embark on an expedition that holds the key to long-term success: entrepreneurship, novelty, strategy, and customer satisfaction. Leveraging this opportunity looming ahead of us, let us emphasize quality control measures as we effortlessly find our way to higher organizational returns.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why do you need an AQA audit?
Audits are frequently performed at predetermined intervals to ensure that an organization’s quality monitoring system is well defined. They can also assist in determining whether or not a company complies with the requirements of a particular quality system.
Why do you need an AQA assessment?
The major purpose of this strategic service is to assess the IT organization’s readiness to deliver an end-to-end enterprise quality management strategy based on business drivers, best practices, and usage patterns, including procedures, people, and technologies.
What is a risk assessment in AQA?
Risk assessment entails categorizing and assessing each risk, as well as calculating the chance and impact of each risk. Other aspects of each risk, such as risk owner, may be evaluated or assigned as part of the risk assessment process.








