According to GM Insights research, we understand that the overall QA market has a positive trend toward rapid development. Its value in 2022 grew to more than $45 billion, and in 2032 it will reach $90 billion with a CAGR of 5%.
The QA industry is not only about direct software testing processes, project management, etc. It’s an extensive set of operations that includes evaluation and planning methods in addition to technical ones. For example, QA audit.Mykhailo PoliarushCEO, ZappleTech Inc.
Zappletech specialists have analyzed the impact of the QA audit report on the future viability of digital products and are ready to share its results with you.
 You will learn from the material the following:
You will learn from the material the following:
- What is a QA audit, and what are the goals of this process.
- How and when a set of these operations is carried out.
- Why outsource QA audit and how it benefits the client.
Table of Contents
What is Quality Assurance Auditing
Let’s start with the basic concept and analyze its role in the QA process.

QA audit is a set of operations party audits carried out throughout the product life cycle. It aims to check and compare specifications, documentation, and processes with business and industry standards.
Overall, it is essential to identify and fix errors in planning and organizing QA, both in manual or QA automation testing services. It also plays a crucial role in facilitating communication and interaction among all project teams: managers, developers, testers, IT architects management system,, designers, etc.
Additionally, QA audit, particularly its technical tools, is part of the Quality Management Software (QMS) complex, which is rapidly expanding in the market. According to Global Data, the QMS industry reached $11.9 billion in 2023. It is expected to grow to $21.4 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 8.8%.
How It Works
QA audit aims to improve the technical condition of a digital product and its compliance with industry standards, target audience expectations, regulatory requirements and brand business logic.
 Thus, the mechanics of a QA audit looks like a combination of clearly defined operations:
Thus, the mechanics of a QA audit looks like a combination of clearly defined operations:
- Assessing the compliance of all components with standards.
- Checking processes and subject behavior.
- Identifying potentially risky elements.
- Gathering data on software interaction principles and its response to queries.
- Evaluating the risks associated with various technical or operational decisions.
- Establishing the level of security for connections, architecture, code, and concept.
- Identifying quality parameters and their adherence to industry-specific standards (ISO, HIPAA, GDPR, etc.).
- Developing methodologies for effectively mitigating potential issues.
- Determining the direction for project modernization, development, and scalability.
As you can see, all these processes have more of an organizational rather than technical nature. However, through the process controls the audit, we can better understand the product’s needs within a specific business context and devise a strategy for ongoing quality control.
Types of Quality Audits
Generally, a QA audit is divided into levels (from individual elements to a comprehensive audit) and types (who conducts the research and under what conditions the audit performed). This allows you to categorize the procedure and determine the service a particular product needs at a certain stage.
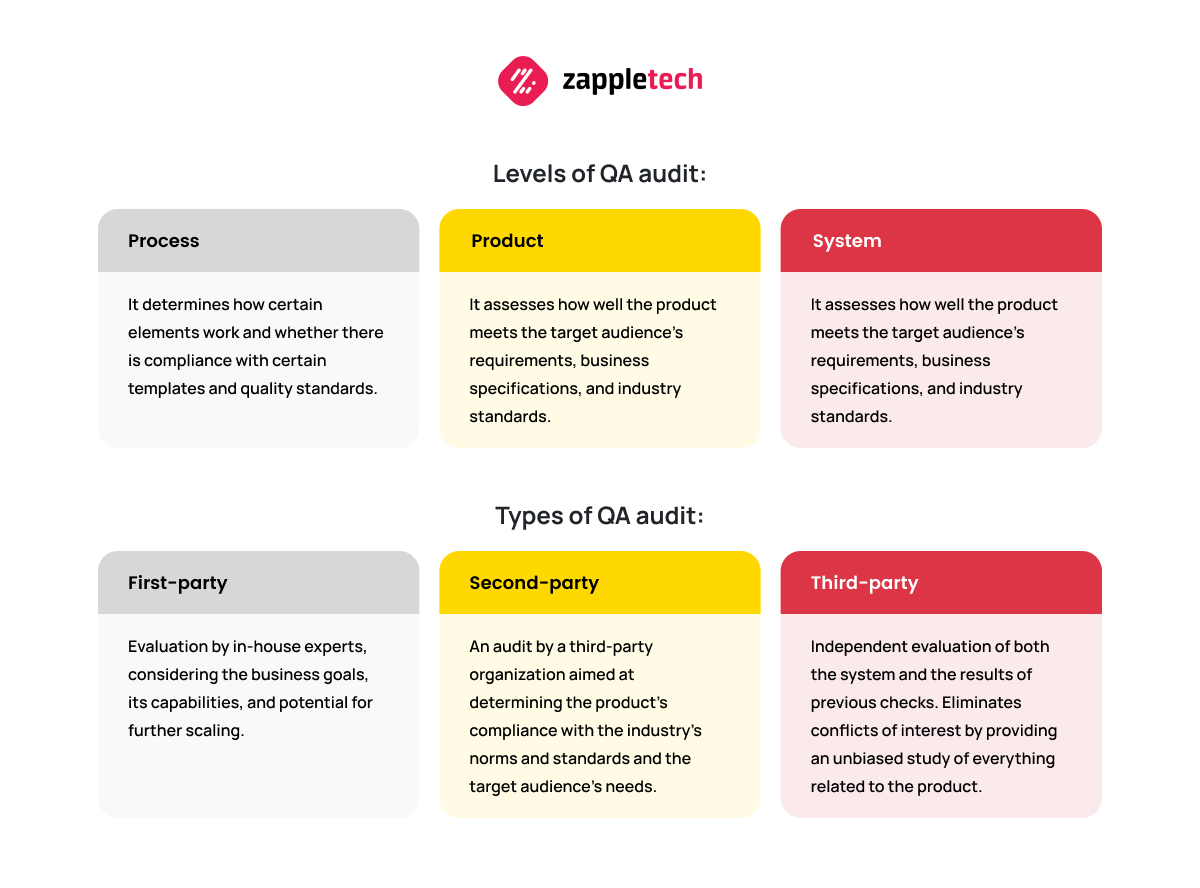 Levels of QA audit:
Levels of QA audit:
- Process. It determines how certain elements work and whether there is compliance with certain templates and quality standards.
- Product. It assesses how well the product meets the target audience’s requirements, business specifications, and industry standards.
- System. All software components and process management methods are checked, and documentation and compliance with regulations and laws are studied.
Types of QA audit:
- First-party. Evaluation by in-house experts, considering the business goals, its capabilities, and potential for further scaling.
- Second-party. An audit by a third-party organization aimed at determining the product’s compliance with the industry’s norms and standards and the target audience’s needs.
- Third-party. Independent evaluation of both the system and the results of previous checks. Eliminates conflicts of interest by providing an unbiased study of everything related to the product.
It is worth combining all of the above for a comprehensive QA audit and quality management system. This is the only way to achieve maximum progress in ensuring quality control and all its components.
Key Objectives within the Quality Assurance Auditing Process

First, let’s define the key stages of the audit process and their goals, i.e., the results we should achieve in the end of system audit.
 There are 6 main steps in a QA audit:
There are 6 main steps in a QA audit:
- Finding performers: First and foremost, it’s important to find experts who will conduct the audit. These can be either fully autonomous organizations specializing in assessments or experts from subcontractor teams, such as Zappletech, an automation testing company.
- Initiating the process: This can be considered a preliminary discussion involving representatives from the audit organizations. At this stage, the work’s scope, timeframe, and extent are defined.
- Preparing for the process: This step involves creating a clear structure for the audit, including a work plan, roadmap, allocation of necessary resources, material and technical tools, methodologies, and so on.
- Conducting the actual audit: A comprehensive set of operations that includes analysis, communication, studying the business logic, and the material and technical foundation of the audited object.
- Analyzing the results: The information obtained during the audit is processed, structured, and reviewed again. Documents are developed that summarize the audit findings, highlight identified issues and provide recommendations for their resolution.
- Addressing the issues: Considering the auditor’s feedback to develop a more efficient working methodology, project development, or complete transformation. Sometimes, this may involve a full product relaunch if it fails to meet specific criteria, standards, industry requirements, and target audience expectations.
As a result, the audit customer receives comprehensive information about the state of the product, its compliance with industry standards, and the target audience’s needs. Also, based on this data, they can design a further action plan to improve the quality system or product and more organically organize related processes, such as development, QA, or scaling.
Why Previous QA Audits did not Lead to Good Results. What Can Be Wrong When Making a QA Audit

Sometimes, things don’t go according to plan, and even considering the audit results doesn’t yield the desired outcomes. There are several reasons for this, such as:
- Lack of experience among auditors in your specific industry.
- Overly complex product or its components.
- Poor organization of the verification process, including lack of communication, ignoring issues, or negligence.
- Low skill levels among the performers.
- Participants in the process lack a clear understanding of the fundamentals of the audit.
- Disregard documentation or market criteria.
There are many more typical problems, but most can be seen as situational. Overall, the quality of the QA audit directly depends on the experience and skills of the contractor performing the process audit. That’s why delegating such projects to independent external experts is recommended.
Strategies for Avoiding These Mistakes
The quality of your audit depends almost entirely on the quality auditing contractor. Therefore, you should choose experienced contractors who will prepare for the audit and help you organize everything.
For the same reason, it is recommended to outsource the audit rather than train your own specialists, spending time, money, and other resources on it.
Benefits of Outsourcing QA Audits. Why It’s Better to Outsource the QA Audit Rather than Do it In-house

External audits and auditors tend to work on many projects, gaining valuable experience that cannot be achieved within one organization, even with intensive training, courses, etc.
 In addition, there are a number of advantages of outsourcing QA audit, for example:
In addition, there are a number of advantages of outsourcing QA audit, for example:
- Minimizing the cost of verification. Training in-house employees specifically for auditing, which involves paying for courses and training, add extra expenses that can be avoided by hiring external experts.
- Reducing subjectivity in audits. Bias from interested parties is usually detrimental to the project’s further development. On the other hand, external experts objectively assess the product, pointing out flaws that pose risks to its viability.
- Improved documentation workflow. Detailed documentation, reporting, and highlighting of results are essential components of an audit. In-house professionals usually lack sufficient experience to effectively document the verification process. Conversely, outsourced contractors are accredited to provide comprehensive information about the product’s state and potential.
- Access to advanced methodologies and skills. While in-house professionals improve their knowledge in one area, external experts have a more comprehensive development. Thus, they better understand AS, IATF, and ISO standards, ensuring a higher quality audit.
- Streamlined coordination of audits. Outsourced contractors have ample experience collaborating for quick and efficient alignment of audit processes. This saves time for your team to focus on critical business operations, enabling a return on investment in hiring auditors and reducing company downtime.
- Value of results. Combining the previous points forms the key advantage of audit outsourcing – the objectivity and expertise of audit results. The information obtained from professional auditors can be used by entrepreneurs to promptly address issues and effectively develop the project, thereby reducing future expenses (or even losses) in the budget.
All the mentioned advantages are provided as examples. In reality, there are many more, especially when hiring experienced auditors. A proper and high-quality QA audit guarantees the competitiveness and viability of a digital product for businesses. This applies to both the early stages of its creation and after release.
How QA Audits are Used in Different Industries
Let’s consider the situation: You are a startup owner and plan to launch a mobile app, let’s say, for audio streaming. You have prepared an idea, a concept, and possibly art (design, visualization) and pre-approved a tech stack. Is this enough to launch a product? Of course not.
 Thanks to the audit, you can check the following:
Thanks to the audit, you can check the following:
- Will your product have demand in the target market?
- Does its concept align with the desires of the target audience?
- Will it be effectively monetized?
- Will there be any issues with international regulators (such as copyrights)?
- Is the chosen tech stack efficient for this type of software?
- Is there potential for further development (scaling) of the product?
You’ll receive more detailed and structured information, including potential risks and controversial issues. This will allow you to analyze the idea better and produce a more optimized digital product that will be in demand in the target market.
How to Check the Contractor when Deciding to Outsource a QA Audit
But before you consider conducting a high-quality audit, focus on choosing a specialist in this process.
An expert with experience in your industry is a top candidate for hiring.Sergey AlmyashevCOO, ZappleTech Inc.
Therefore, first of all, find out about the experience of a potential project executor by checking out the portfolio and reviews on Clutch, G2, Good Firms, Design Rush, etc.
Also, don’t forget to visit the company’s official website, where reports with the results of past internal audits are often published (of course, without details due to NDA).
If you are satisfied with the candidate, contact the company representative and discuss the project.
The Difference Between a Good QA Audit and a Bad QA Audit

Usually, it’s not possible to distinguish between a bad internal audit and a good audit at first glance. However, Zappletech experts identify several indicators that suggest the audit results may be questionable. For example:
- Inadequate documentation of the process.
- Lack of initiative from the auditors.
- Poor communication with representatives of the project being audited.
- Clear disregard for standards or norms.
- Ignoring market research and the target audience.
- Absence of a clearly defined audit strategy.
In the long run, a poor audit will bring additional problems: increased maintenance costs (for upgrades or even a complete product relaunch), difficulties in software licensing, customer requirements and conflicts with regulators and publishers of digital solutions.
Therefore, the best option is to hire professionals to conduct the audit and thoroughly test your project to ensure its quality.
Why You Should Order an Audit in Zappletech
A digital product is an investment in brand development, competitiveness, and market viability. That’s why its quality is key in shaping a positive business image.
Zappletech specialists have been providing comprehensive QA services, including auditing digital solutions, for many years. If you want to provide your project with quality support throughout its life cycle, delegate this task to professionals.Mikhail BodnarchukCDO, ZappleTech Inc.
Zappletech experts will comprehensively audit your idea, IT product, or business and help you improve all aspects! Feel free to contact the company manager to discuss the project!