Table of Contents
Introduction
More teams and organizations embrace test automation, they will require the right tools and skills and the right test automation strategy. Since automation requires multiple tools, frameworks, and programming languages to accomplish its goals, imposing organization and an overarching strategy for all testing efforts becomes a critical focal point.
If you want to know how to automate your tests and how to eliminate human involvement, you need to understand the automation test process. In this article, we will explore the right strategy for building an automation testing strategy and the key challenges you may encounter.
Key elements of the automation testing process
To set up an effective automation system, you need to take a lot of things into account. Here is a brief list of what to pay attention to.
Defining the scope and goals
To make an automation testing process, it’s important to start with a clear understanding of what is being automated and what the goals of the automation are. This can be done by defining what the software is supposed to do and what the user is trying to accomplish.
Next, you need to identify the automation steps and decide on what criteria the tests should be run. You will need to decide on inputs, expected outputs and expected results. Later, you will need to choose the automation environment and define how the automation should run, which tool you will be using, and what automation scripts you will be writing.
Establishing the test approach
Once a team has decided on which testing approach they will use, they must then decide how to structure the test approach. The most effective way to do this is to utilize the testing pyramid. The test automation pyramid lays out the types of tests to be included in an automated test suite.
The bottom of the pyramid is for the highest level of automation, unit tests. The next level up is integration tests. The next level up is functional tests. These tests can be run in a few minutes or less. The highest level is end-to-end tests.

The pyramid outlines the different types of automated tests that should be included in a test suite. It also lays out the sequence and frequency of the tests.
Selecting the right tools
The successful implementation of the automation testing strategy entirely depends on the tools chosen for its realization. Here are some criteria to follow when deciding on the tech stack:
- Ease of use. To decrease the human involvement and time spending it should be easy to write and maintain the testing scripts.
- Low entry barrier. Running the test suites should be simple so that any team member was able to run them whenever possible, and manual testers could adapt to using them.
- Support of necessary environment. If you are building a cross-platform app, your automation tool should be compatible with all operating systems you need.
- Test reporting feature. The tool should be able to generate comprehensive test reports that will be easy to understand for the management team and business owner.
Designing test cases
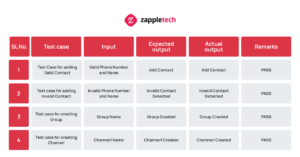
After determining the test approach and picking the tools, start designing test cases to be executed. At this point, if a team is new to test automation, it would be best to approach individuals with experience in automation for initial guidance. Some test automation steps for developing test cases:
1) Create reusable scripts
Test cases should be created at the beginning of a project and should be reused, instead of constantly developing new ones. This can be achieved by creating a template that is set up in a standard way. Establishing a template and using it throughout a project saves time and effort. Ensure that a template is created that is appropriate for the needs of your project and the skill level of your team.
2) Make the scripts comprehensive
When building a test plan, it is important to establish a clear test approach so that the team will know what the test is trying to do. One approach is to create a table that outlines what success criteria the test is trying to fulfil and what the expected outcome is. Another approach is to create a table that outlines how the test should be executed.
3) Prioritize the tests
It is important to establish a test approach that will help you prioritize tests in the hierarchy. Just like you have a hierarchy of features and software components, you also have a hierarchy of tests. These tests need to be prioritized because they have different levels of impact on the overall project.
Create execution plan
After test cases have been designed and tested, the next step is to create the test execution plan. This plan will define the order in which all the test cases will be run, as well as the duration of each test case, and when they will be run. The test execution plan will also describe what will happen if a test case fails.
It’s a good practice to establish a set of day-to-day tasks and processes for your test automation development. This can be done by developing a CI/CD pipeline. This will establish the process from pushing code to version control, running it through a set of tests, integrating it, and keeping the build up-to-date with the latest test results.
Review test results
You should review the test results a few days after the test is complete. This will provide you with a clear understanding of the success of the test and will allow you to resolve any issues that may have occurred. The test results can be reviewed and fixed as a part of the regular pipeline, or they can be reviewed in a separate testing review meeting.
After the first set of tests has been run, QAs can take a step back and review the test results with stakeholders. This can be done in the form of a meeting or a report, with each stakeholder providing feedback on what they thought of the test results and the process. This feedback can then be used to make changes in the process, such as adding more time to certain test suites or removing them.
The main challenges in test automation process
Automation testing is a wellhead of benefits on the condition that it is properly implemented. That is why it is important to know not only the advantages but also the pitfalls that QA teams face while shifting to automation testing.
Significant investment
When it comes to test automation, there are some significant initial investments that the management team has to make. These investments are quite costly and not one-time ones, but they are necessary in order to make a company more efficient, accurate and productive in the long run.
High barrier of entry
To succeed in automation testing, the engineer must have a strong background with knowledge of programming languages and corresponding technologies. Besides, great experience is necessary to set up the automation testing process from scratch.
Exaggerated expectations
Test automation is a great way to speed up the testing process, but it is a mistake to expect it to be the answer to all QA problems. To maximize efficiency, it is important to set realistic goals and understand that the software can’t be fully covered with automation. Moreover, even the working testing scripts should be constantly monitored and updated.
Test maintenance
The main challenge in test automation is maintainability. Test automation is a continuous process. New requirements, changes in the software, and new technologies are constantly introduced. In order to avoid failures in the future, the scripts should be constantly maintained and updated.
Tool selection
When it comes to selecting a technology stack for automation testing there are a few challenges that companies may encounter. Some of these challenges include the need to find a tool that is user-friendly, affordable, has a learning curve that can be overcome relatively quickly, and is able to be integrated with other tools that a company already has.
The company also needs to consider the tools they already have in place, their current real-time needs, their ability to provide support for the tool, and whether the tool has the ability to be adopted for any future projects.
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed our article about automation. We want to help you build a scalable automation process in software testing that will eliminate human involvement for good. Please contact us anytime if you have any questions. Our specialists will give you a free consultation where we explore the possible options and help you to choose the best one.